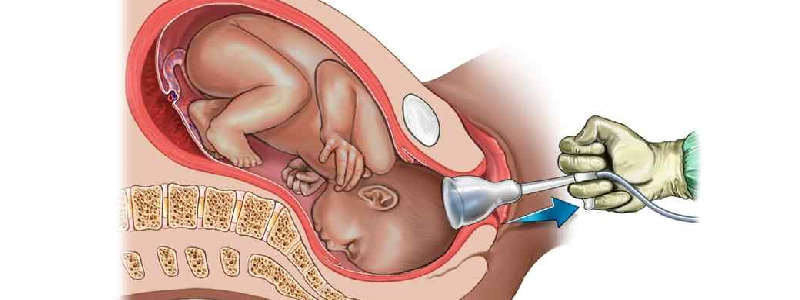
Instrumental birth, also known as assisted vaginal delivery, refers to the method of childbirth in which medical instruments are used to assist in the delivery of the baby. It is a procedure that is employed when the mother is unable to deliver the baby effectively on her own or when there are concerns for the well-being of the mother or baby. In this article, we will explore the reasons for instrumental birth, the different techniques used, and the potential benefits and risks associated with this procedure.
There are various reasons why instrumental birth may be recommended by healthcare providers. Some common indications include prolonged labor, fetal distress, maternal exhaustion, maternal health conditions, or the need for a speedy delivery due to certain medical concerns. In these situations, the use of instruments can help expedite the birth process and ensure the safe delivery of the baby.
Two primary instruments used in instrumental birth are forceps and vacuum extractors. Forceps are metal instruments resembling large spoons or tongs that are carefully placed around the baby's head to aid in guiding and assisting its passage through the birth canal. Vacuum extractors, on the other hand, are suction devices that are attached to the baby's head to provide traction and assist in its delivery.
During an instrumental birth, the healthcare provider carefully assesses the position and station of the baby's head in the birth canal. They then select the appropriate instrument based on the specific circumstances and the mother's condition. Before proceeding, the healthcare provider ensures that the mother is adequately numbed with anesthesia or pain relief medication to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
The use of instruments during childbirth can have potential benefits. It can help avoid the need for a more invasive cesarean section in certain situations, providing a vaginal birth experience for the mother. Instrumental birth can also reduce the risks associated with prolonged labor, such as maternal exhaustion or increased chances of infection. Furthermore, it may aid in the prompt delivery of a baby experiencing fetal distress, improving their overall well-being.
However, instrumental birth is not without risks or potential complications. The mother may experience vaginal tears or lacerations due to the use of instruments. There is also a higher risk of damage to the perineum or pelvic floor muscles. In some cases, the baby may develop temporary bruising or swelling on the head due to the pressure exerted by the instruments. Additionally, there is a slight increase in the risk of fetal injury, although serious complications are relatively rare.
After an instrumental birth, both the mother and baby are closely monitored for any signs of complications or adverse effects. The mother may require stitches or sutures to repair any tears or lacerations. The baby's condition is assessed to ensure they are transitioning well and there are no immediate concerns.
It is important to note that instrumental birth is a medical intervention that is employed when necessary for the well-being of the mother or baby. The decision to proceed with instrumental delivery is made on an individual basis, taking into consideration the specific circumstances and risks involved. Healthcare providers carefully weigh the potential benefits against the possible risks and make decisions in the best interest of the mother and baby.
In conclusion, instrumental birth is a method of childbirth that involves the use of medical instruments to assist in the delivery of the baby. It is recommended in certain situations where the mother is unable to deliver the baby effectively or when there are concerns for the well-being of the mother or baby. While instrumental birth can have potential benefits, it is not without risks or potential complications. Healthcare providers carefully assess each case and make decisions to ensure the safe and successful delivery of the baby.
